“CentOS服务搭建-04-运用FRPS服务搭建黑群晖NAS的FRPC”的版本间的差异
(→《frps.service》文档) |
|||
| (未显示同一用户的57个中间版本) | |||
| 第1行: | 第1行: | ||
[[category:IS]] | [[category:IS]] | ||
| − | = | + | * FRP (Fast Reservation Protocol高性能反向代理应用):可以帮助您轻松地进行内网穿透,对外网提供服务,支持 tcp, http, https 等协议类型,并且 web 服务支持根据域名进行路由转发。 |
| + | * 作用 | ||
| + | ** 利用处于内网或防火墙后的机器,对外网环境提供 http 或 https 服务。 | ||
| + | ** 对于 http 服务支持基于域名的虚拟主机,支持自定义域名绑定,使多个域名可以共用一个80端口。 | ||
| + | ** 利用处于内网或防火墙后的机器,对外网环境提供 tcp 服务,例如在家里通过 ssh 访问处于公司内网环境内的主机。 | ||
| + | ** 可查看通过代理的所有 http 请求和响应的详细信息。(待开发) | ||
| + | |||
| + | =CentOS 7安装frps端= | ||
* 本次安装服务应用于群晖系统,客户端为frpc0.26.0,因此,frps端使用同版本 | * 本次安装服务应用于群晖系统,客户端为frpc0.26.0,因此,frps端使用同版本 | ||
# su获取root | # su获取root | ||
# wget https://github.com/fatedier/frp/releases/download/v0.26.0/frp_0.26.0_linux_amd64.tar.gz | # wget https://github.com/fatedier/frp/releases/download/v0.26.0/frp_0.26.0_linux_amd64.tar.gz | ||
| + | # wget https://github.com/fatedier/frp/releases/download/v0.53.2/frp_0.53.2_linux_amd64.tar.gz | ||
| + | # wget https://github.com/fatedier/frp/releases/download/v0.52.3/frp_0.52.3_linux_amd64.tar.gz | ||
# 解压:tar xf frp_0.26.0_linux_amd64.tar.gz | # 解压:tar xf frp_0.26.0_linux_amd64.tar.gz | ||
# 改名:mv frp_0.26.0_linux_amd64 frp | # 改名:mv frp_0.26.0_linux_amd64 frp | ||
| 第11行: | 第20行: | ||
# 配置文件:vim frps.ini | # 配置文件:vim frps.ini | ||
# 编辑ini文件 按ins进入编辑(精简) | # 编辑ini文件 按ins进入编辑(精简) | ||
| − | <pre> | + | |
| − | + | ==《frps.ini》文档== | |
| − | [common] | + | <pre>[common] |
| − | bind_addr = | + | bind_addr = xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx # frps内网服务器地址,如果有防火墙的话,设置下述端口映射 |
| − | bind_port = | + | bind_port = xxxxx # frps服务端口 |
| − | vhost_http_port = xxxxx | + | bind_udp_port = xxxx # udp服务端口 |
| − | vhost_https_port = xxxxx | + | vhost_http_port = xxxxx # http服务端口 |
| − | privilege_token = | + | vhost_https_port = xxxxx # https服务端口 |
| − | dashboard_port = xxxx | + | privilege_token = xxxxxxxx # 握手密钥 |
| − | dashboard_user = xxxxx | + | subdomain_host = xxxx.xxx # 填写顶级域名,意味着对应frpc的2级域名代理启用 |
| − | dashboard_pwd = xxxxxxx | + | dashboard_port = xxxx # 服务器面板端口 |
| − | + | dashboard_user = xxxxx # 服务器面板用户 | |
| + | dashboard_pwd = xxxxxxx # 服务器面板密码 | ||
| + | log_file = ./frpslog.log | ||
| + | log_level = info | ||
| + | log_max_days = 3 | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | 临时运行:./frps -c ./frps.ini | + | ==frps的调试== |
| − | + | # 临时运行:<pre> ./frps -c ./frps.ini</pre> | |
| − | 命令启动之后如果不重启VPS就会一直运行,以下操作可以省略。只需要在服务器重启之后,重新cd到程序目录,输入一次nohup ./frps -c ./frps.ini &命令即可 | + | # 一次性开机运行:nohup ./frps -c ./frps.ini & |
| + | #: 命令启动之后如果不重启VPS就会一直运行,以下操作可以省略。只需要在服务器重启之后,重新cd到程序目录,输入一次nohup ./frps -c ./frps.ini &命令即可 | ||
| + | # 停止:先找到这个进程,使用ps -ef 查看进程ID <pre>ps -aux | grep frp</pre> | ||
| + | # 然后:kill -9 PID | ||
| − | + | ==frps.service自启动文档== | |
| − | + | # 新建frps目录:mkdir /etc/frps | |
| − | + | # mkdir /usr/etc/frps | |
| + | # 拷贝frps.ini 到/etc/frps:cp /源目录/frps.ini /etc/frps/ | ||
| + | # 拷贝frps到/usr/etc/frps:cp /源目录/usr/etc/frps | ||
| + | # frps.service文档保存于:/etc/systemd/system/ | ||
| + | # 使用systemd配置开机自启(适用于 centos7 Ubuntu 16 或 debian 8) <pre> sudo vim /etc/systemd/system/frps.service 新建此文件,并写入以下内容</pre> | ||
| − | + | ===《frps.service》文档=== | |
| − | + | # 注意点:/usr/etc/frps 为服务端frps的执行文件目录(可自定义) | |
| − | + | # 注意点:/etc/frps/frps.ini 为服务端frps.in配置文档目录(可自定义) | |
| − | + | <pre> | |
| − | + | [Unit] | |
| + | Description=frps Dgn | ||
| + | After=network.target | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[Service] | [Service] | ||
Type=simple | Type=simple | ||
| − | ExecStart=/usr/etc/frps/frps -c /etc/ | + | # User=root |
| − | # /usr/etc/frps | + | ExecStart=/usr/etc/frps/frps -c /etc/frps_aker/frps.ini |
| + | # /usr/etc/frps 文件目录,注意service文件中要指向frps运行程序(这个没查到网上解释,以为只要放个空文档,其实要放入执行文件,搞了半天才运行成功!!!) | ||
# /etc/frps/frps.ini 配置目录 | # /etc/frps/frps.ini 配置目录 | ||
| + | |||
[Install] | [Install] | ||
WantedBy=multi-user.target | WantedBy=multi-user.target | ||
| − | + | </pre> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | 启动并设为开机自启。 | + | ===frps.service自启动=== |
| + | # vim编辑退出:Esc,# :wq(保存退出) | ||
| + | # 启动并设为开机自启。 | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
sudo systemctl start frps | sudo systemctl start frps | ||
| + | # (把start改为stop即终止frps) | ||
sudo systemctl enable frps | sudo systemctl enable frps | ||
| − | + | systemctl status frps | |
| − | + | # 查看frps状态 | |
| − | + | </pre> | |
| − | vi /etc/rc.local | + | * Centos6.5及以下版本frps自启动 |
| − | 在最下面加一行/usr/sbin/frp/frps -c /usr/sbin/frp/frps.ini | + | # vi /etc/rc.local |
| − | 其中 /usr/sbin/frp是程序放置的目录,自己修改,重启ok | + | # 在最下面加一行/usr/sbin/frp/frps -c /usr/sbin/frp/frps.ini |
| + | # 其中 /usr/sbin/frp是程序放置的目录,自己修改,重启ok | ||
| − | + | ===frps.service自启动进程查看=== | |
| − | + | # 查看frp是否启动:ps aux | grep frps | |
| − | 查看frp启动状态 | + | # 查看frp启动状态 <pre>sudo systemctl status frps</pre> |
| − | sudo systemctl status frps | ||
| − | + | ==frps服务下的防火墙端口开启== | |
| − | + | * 开启端口 | |
| − | firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=xxxx/tcp # | + | <pre> |
| − | firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=xxxx/tcp # | + | firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=xxxx/tcp # 开放bind_port(frps服务)# 必须 |
| + | firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=xxxx/tcp # 开放dashboard_port(服务面板http)# 必须 | ||
| + | firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=xxxx/tcp # 开放vhost_http_port(http端口)# 按需 | ||
| + | firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=xxxx/tcp # 开放vhost_http_port(https端口)# 按需 | ||
| + | firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=xxxx/tcp # 开放bind_udp_port端口(udp直连)# 按需 | ||
| + | firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=xxxx/tcp # 开放kcp_bind_port端口(kcp端口)# 按需 | ||
firewall-cmd --reload #重启防火墙(修改配置后要重启防火墙) | firewall-cmd --reload #重启防火墙(修改配置后要重启防火墙) | ||
firewall-cmd --list-all # 查看防火墙规则 | firewall-cmd --list-all # 查看防火墙规则 | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | * ssh端口开启(按需):公网服务器防火墙允许对应端口的流量通过,所以需要配置防火墙: | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=10067/tcp --permanent | ||
| + | firewall-cmd --reload | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | * 内网机器上面执行 tail -f nohup.out 查看启动命令的执行结果akerlu | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===firewall常用命令=== | ||
| + | * 安装firewall命令 | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | yum install firewalld firewalld-config | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | * Firewall开启常见端口命令 | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=80/tcp --permanent | ||
| + | firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=443/tcp --permanent | ||
| + | firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=22/tcp --permanent | ||
| + | firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=53/udp --permanent | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | * Firewall关闭常见端口命令 | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | firewall-cmd --zone=public --remove-port=80/tcp --permanent | ||
| + | firewall-cmd --zone=public --remove-port=443/tcp --permanent | ||
| + | firewall-cmd --zone=public --remove-port=22/tcp --permanent | ||
| + | firewall-cmd --zone=public --remove-port=53/udp --permanent | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | * 指定特定源IP访问某端口 | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | firewall-cmd --permanent --add-rich-rule="rule family="ipv4" source address="192.168.100.1" port protocol="tcp" port="80" accept" | ||
| + | #添加源IP 192.168.100.1访问80端口 | ||
| + | firewall-cmd --permanent --add-rich-rule="rule family="ipv4" source address="192.168.100.0/24" port protocol="tcp" port="80" accept" | ||
| + | #添加IP段访问80端口 | ||
| + | firewall-cmd --permanent --remove-rich-rule="rule family="ipv4" source address="192.168.100.1" port protocol="tcp" port="80" accept" | ||
| + | #删除源IP 192.168.100.1访问80端口 | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | * 指定特定源IP开放所有端口 | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | firewall-cmd --permanent --add-rich-rule="rule family="ipv4" source address="192.180.10.10" accept" | ||
| + | firewall-cmd --reload | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | * 批量添加区间端口 | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=4400-4600/udp --permanent | ||
| + | firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=4400-4600/tcp --permanent | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | * 查看端口列表: | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | firewall-cmd --permanent --list-ports | ||
| + | firewall-cmd --permanent --list-all | ||
| + | firewall-cmd --permanent --list-rich-rules | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | * 其他常用命令 | ||
| + | ** 启动服务:systemctl start firewalld | ||
| + | ** 关闭服务:systemctl stop firewalld | ||
| + | ** 重启服务:systemctl restart firewalld、firewall-cmd --reload | ||
| + | ** 查看服务状态:systemctl status firewalld、firewall-cmd --state | ||
| + | ** 开机自启服务:systemctl enable firewalld | ||
| + | ** 开机禁用服务:systemctl disable firewalld | ||
| + | ** 查看是否开机自启:systemctl is-enable firewalld | ||
| + | |||
| + | =NAS端安装FRPC= | ||
| + | # 下载安装docker | ||
| + | # docker注册表,选用frpc 0.26.0版本(可自行选择容易下载的版本,但服务端frps必须对应同版本或者同大版本号的,如:0.34.1的话,可以用0.34.2) | ||
| + | # docker注册表下载后,在映像中可以看到。选择映像中的frpc进行启动编辑,启动编辑省略,可以参考github中的导航说明。 | ||
| + | # 配置frpc.ini,本次基于frpc 0.26.0版本 | ||
| + | <gallery> | ||
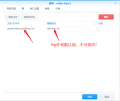
| + | 20201222135026.png|frpc容器配置注意 | ||
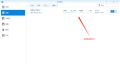
| + | 20201222135035.png|frpc容器配置成功 | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==《frpc.ini》文档== | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | [common] | ||
| + | server_addr = xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx | ||
| + | # 服务器地址 | ||
| + | server_port = xxxx | ||
| + | # 服务器端口 | ||
| + | privilege_token = xxxxxx | ||
| + | # token = xxxxxx 有些服务端版本采用这个字节,多数采用“privilege_token”字节,token理解为密码 | ||
| + | protocol = tcp | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http] | ||
| + | type = http | ||
| + | # http协议orhttps协议,如果两个都要的话就单独复制一段[https] | ||
| + | local_ip = 192.168.x.xx | ||
| + | # 群晖的内网IP | ||
| + | local_port = xxxxx | ||
| + | # 你自己的web服务器端口 | ||
| + | custom_domains = xxxxxxx.xxx | ||
| + | # 如果你有自己的域名,可以设置你自己的域名,先将自己的顶级域名解析到frp服务器域名(如二级域名的话用CNAME记录,不要用A记录) | ||
| + | #subdomain = nas | ||
| + | # 全局下唯一的子域名,你的访问地址将会是http://subdomain.xxx.xxx,服务器端必须已绑定顶级域名,否则不要设置; | ||
| + | # 此外,顶级域名需要在域名系统上做好CNAME的泛解析,否则不可用。HOST:*.xxx.xxx;Value:xxx.xxx。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | [ssh] | ||
| + | type = tcp | ||
| + | local_ip = 192.168.x.xxx | ||
| + | local_port = xxxxxx | ||
| + | # 需要转发到的端口,ssh端口默认是22 | ||
| + | remote_port = xxxxxx | ||
| + | # frp服务端的远程监听端口,即你访问服务端的remote_port就相当于访问客户端的 local_port,如果填0则会随机分配一个端口 | ||
| + | |||
| + | #[DSM] | ||
| + | # type = tcp # tcp协议 | ||
| + | # local_ip = 192.168.x.xxx | ||
| + | # 127.0.0.1指穿透本机,也可以填写群晖内网IP. | ||
| + | # local_port = xxxxxx | ||
| + | # 群晖内网HTTP端口,默认为5000. | ||
| + | # remote_port = xxxx | ||
| + | # 映射到外网端口,暴露给服务器,这个客户端必须唯一 | ||
| + | # subdomain = nas | ||
| + | # 全局下唯一的子域名,你的访问地址将会是http://subdomain.xxx.xxx,服务器端必须已绑定顶级域名,否则不要设置; | ||
| + | # 此外,顶级域名需要在域名系统上做好CNAME的泛解析,否则不可用。HOST:*.xxx.xxx;Value:xxx.xxx。 | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| − | + | =搭建手记= | |
| − | + | 大鹿搭建frp反向代理服务的背景: | |
| − | # | + | * 一台私有nas需要安装在农村老家的东方有线光纤宽带下,而经过确认和尝试,获取的DDNS是111.214的,也就是东方有线的私网,无法穿透。 |
| − | # | + | * 和东方有线在自家院子里冒着12月的寒风电话沟通三巡,无法提供公网IP,哪怕是动态的,似乎他们的客服完全不懂,此处万马奔腾…… |
| + | * 晚上在网上查询了多种方法,其中花生壳的付费和硬件模式(花生棒、花生盒子)想过尝试,但是最终还是不能接受这种太过受制于人的方式。 | ||
| + | * 最终发现了frp这个从不知道的事物。初步构想是在晚上躺在农村的床上想到的:企业固定IP + 自建的CentOS,或者上海市区的电信公网IP(市区里装的早,刚发现提供了公网IP,良心!)两套方案,最终决定第一种。 | ||
| + | * 周末后周一到公司,利用非工作的午休和晚间时间,启动了安装和搭建调试: | ||
| + | # NAS搭建docker以及docker容器的frpc; | ||
| + | # CentOS本来是当热备机和bbs服务器的,负载几乎是0.x%级别的,所以通过内网ssh搭建了frps; | ||
| + | # CentOS开放firewall; | ||
| + | # AF开放frps端口; | ||
| + | # 当晚宿舍调试握手,成功! | ||
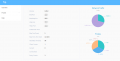
| + | # 第二日,记录了本次搭建和调试的笔记,或许哪一天我的孩子或者朋友需要参考。<gallery>20201222141012.png|frps服务面板</gallery> | ||
| − | + | ==2021/12/1后记== | |
| + | * 将自家一台闲置的G41主板GAMEMAX机箱的主机做成了群晖NAS,需要同时请求Centos的FRP代理. | ||
| + | * 产生的问题就是FRPS的http类监听端口只有各一个(http、https),而处于app需求,每台nas都需要占用http两个端口。 | ||
| + | * 如何实现两台nas的代理需求困扰了两天,尝试了网上数个谬误的推荐,本人也不清楚博主最后是否运行稳定了多久…… | ||
| + | # 谬误1:取消frps端vhost监听,使用frpc的remote_host访问……,其实从原理上就是不可能的;当然,大鹿在当时无计可施情况下也试了几次,失败; | ||
| + | # 谬误2:不使用type=http,改为type=tcp……,协议上来讲tcp和http协议是有区别的,如果偶尔成功了也只能说是基础协议层面的bug类问题,我尝试过,但是最后还是不稳定放弃了。 | ||
| + | * 最终使用了如下方案: | ||
| + | # 域名服务启用CNAME泛解析,HOST:*.xxx.xxx;Value:xxx.xxx; | ||
| + | # FRPS启用:subdomain_host; | ||
| + | # FRPC启用:subdomain。 | ||
| + | * 目前为止其中一台nas成功启用frp服务,另外一台在本周更新frpc和docker,因为设备在100多公里外:) | ||
| + | ==2021/12/6多http及ssh服务的问题解决== | ||
| + | * 上周将第二台接入后,第一台无法联机,怀疑还是配置问题。回家后还发现NAS的电源出问题了,似乎是损毁了。 | ||
| + | * 重新购买电源,更换后还是无法使用subdomain登陆。 | ||
| + | * 经过多轮调试和查询FRPS服务说明文档,今天问题发现并解决,属于多台客户端的frpc配置重定义问题: | ||
| + | # 多台frpc中[common]定义不用变化; | ||
| + | # 多台客户机frpc中[http]、[https]、[ssh]等协议代理请求中不能使用重名。比如使用http和ssh的: | ||
| + | ## [http-1]、[http-2]、[https-1]、[https-2]; | ||
| + | ## [ssh-1]、[ssh-2]。 | ||
| + | # 以上修正后,所有访问正常,其他协议类定义可以推断同样依次类推。 | ||
| + | # 注意:务必要在FRPS和FRP中定义:<subdomain>。 | ||
| + | * 其实从理论上也可以理解,如果协议的代理请求是同样[ID],FRPS服务器确实如何去识别这是谁的要求呢? | ||
| + | * 自此,多台frpc的代理服务配置完成,结案。 | ||
| + | * 总结:所有的开发源代码的应用,多参照说明文档,少看网络上那些假大神的瞎捣鼓,看还是要看看,走走弯路也可以学到知识。 | ||
| + | ==关于nas也可以借助FRPS运用远程ssh进行完全管理== | ||
| + | * 可参考[[CentOS服务搭建-03-开启SSH服务]] | ||
2024年1月12日 (五) 12:14的最新版本
- FRP (Fast Reservation Protocol高性能反向代理应用):可以帮助您轻松地进行内网穿透,对外网提供服务,支持 tcp, http, https 等协议类型,并且 web 服务支持根据域名进行路由转发。
- 作用
- 利用处于内网或防火墙后的机器,对外网环境提供 http 或 https 服务。
- 对于 http 服务支持基于域名的虚拟主机,支持自定义域名绑定,使多个域名可以共用一个80端口。
- 利用处于内网或防火墙后的机器,对外网环境提供 tcp 服务,例如在家里通过 ssh 访问处于公司内网环境内的主机。
- 可查看通过代理的所有 http 请求和响应的详细信息。(待开发)
目录
CentOS 7安装frps端
- 本次安装服务应用于群晖系统,客户端为frpc0.26.0,因此,frps端使用同版本
- su获取root
- wget https://github.com/fatedier/frp/releases/download/v0.26.0/frp_0.26.0_linux_amd64.tar.gz
- wget https://github.com/fatedier/frp/releases/download/v0.53.2/frp_0.53.2_linux_amd64.tar.gz
- wget https://github.com/fatedier/frp/releases/download/v0.52.3/frp_0.52.3_linux_amd64.tar.gz
- 解压:tar xf frp_0.26.0_linux_amd64.tar.gz
- 改名:mv frp_0.26.0_linux_amd64 frp
- 进入目录:cd frp
- 删除没用的客户端文件:rm -f frpc*
- 配置文件:vim frps.ini
- 编辑ini文件 按ins进入编辑(精简)
《frps.ini》文档
[common] bind_addr = xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx # frps内网服务器地址,如果有防火墙的话,设置下述端口映射 bind_port = xxxxx # frps服务端口 bind_udp_port = xxxx # udp服务端口 vhost_http_port = xxxxx # http服务端口 vhost_https_port = xxxxx # https服务端口 privilege_token = xxxxxxxx # 握手密钥 subdomain_host = xxxx.xxx # 填写顶级域名,意味着对应frpc的2级域名代理启用 dashboard_port = xxxx # 服务器面板端口 dashboard_user = xxxxx # 服务器面板用户 dashboard_pwd = xxxxxxx # 服务器面板密码 log_file = ./frpslog.log log_level = info log_max_days = 3
frps的调试
- 临时运行:
./frps -c ./frps.ini
- 一次性开机运行:nohup ./frps -c ./frps.ini &
- 命令启动之后如果不重启VPS就会一直运行,以下操作可以省略。只需要在服务器重启之后,重新cd到程序目录,输入一次nohup ./frps -c ./frps.ini &命令即可
- 停止:先找到这个进程,使用ps -ef 查看进程ID
ps -aux | grep frp
- 然后:kill -9 PID
frps.service自启动文档
- 新建frps目录:mkdir /etc/frps
- mkdir /usr/etc/frps
- 拷贝frps.ini 到/etc/frps:cp /源目录/frps.ini /etc/frps/
- 拷贝frps到/usr/etc/frps:cp /源目录/usr/etc/frps
- frps.service文档保存于:/etc/systemd/system/
- 使用systemd配置开机自启(适用于 centos7 Ubuntu 16 或 debian 8)
sudo vim /etc/systemd/system/frps.service 新建此文件,并写入以下内容
《frps.service》文档
- 注意点:/usr/etc/frps 为服务端frps的执行文件目录(可自定义)
- 注意点:/etc/frps/frps.ini 为服务端frps.in配置文档目录(可自定义)
[Unit] Description=frps Dgn After=network.target [Service] Type=simple # User=root ExecStart=/usr/etc/frps/frps -c /etc/frps_aker/frps.ini # /usr/etc/frps 文件目录,注意service文件中要指向frps运行程序(这个没查到网上解释,以为只要放个空文档,其实要放入执行文件,搞了半天才运行成功!!!) # /etc/frps/frps.ini 配置目录 [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
frps.service自启动
- vim编辑退出:Esc,# :wq(保存退出)
- 启动并设为开机自启。
sudo systemctl start frps # (把start改为stop即终止frps) sudo systemctl enable frps systemctl status frps # 查看frps状态
- Centos6.5及以下版本frps自启动
- vi /etc/rc.local
- 在最下面加一行/usr/sbin/frp/frps -c /usr/sbin/frp/frps.ini
- 其中 /usr/sbin/frp是程序放置的目录,自己修改,重启ok
frps.service自启动进程查看
- 查看frp是否启动:ps aux | grep frps
- 查看frp启动状态
sudo systemctl status frps
frps服务下的防火墙端口开启
- 开启端口
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=xxxx/tcp # 开放bind_port(frps服务)# 必须 firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=xxxx/tcp # 开放dashboard_port(服务面板http)# 必须 firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=xxxx/tcp # 开放vhost_http_port(http端口)# 按需 firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=xxxx/tcp # 开放vhost_http_port(https端口)# 按需 firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=xxxx/tcp # 开放bind_udp_port端口(udp直连)# 按需 firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=xxxx/tcp # 开放kcp_bind_port端口(kcp端口)# 按需 firewall-cmd --reload #重启防火墙(修改配置后要重启防火墙) firewall-cmd --list-all # 查看防火墙规则
- ssh端口开启(按需):公网服务器防火墙允许对应端口的流量通过,所以需要配置防火墙:
firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=10067/tcp --permanent firewall-cmd --reload
- 内网机器上面执行 tail -f nohup.out 查看启动命令的执行结果akerlu
firewall常用命令
- 安装firewall命令
yum install firewalld firewalld-config
- Firewall开启常见端口命令
firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=80/tcp --permanent firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=443/tcp --permanent firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=22/tcp --permanent firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=53/udp --permanent
- Firewall关闭常见端口命令
firewall-cmd --zone=public --remove-port=80/tcp --permanent firewall-cmd --zone=public --remove-port=443/tcp --permanent firewall-cmd --zone=public --remove-port=22/tcp --permanent firewall-cmd --zone=public --remove-port=53/udp --permanent
- 指定特定源IP访问某端口
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-rich-rule="rule family="ipv4" source address="192.168.100.1" port protocol="tcp" port="80" accept" #添加源IP 192.168.100.1访问80端口 firewall-cmd --permanent --add-rich-rule="rule family="ipv4" source address="192.168.100.0/24" port protocol="tcp" port="80" accept" #添加IP段访问80端口 firewall-cmd --permanent --remove-rich-rule="rule family="ipv4" source address="192.168.100.1" port protocol="tcp" port="80" accept" #删除源IP 192.168.100.1访问80端口
- 指定特定源IP开放所有端口
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-rich-rule="rule family="ipv4" source address="192.180.10.10" accept" firewall-cmd --reload
- 批量添加区间端口
firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=4400-4600/udp --permanent firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=4400-4600/tcp --permanent
- 查看端口列表:
firewall-cmd --permanent --list-ports firewall-cmd --permanent --list-all firewall-cmd --permanent --list-rich-rules
- 其他常用命令
- 启动服务:systemctl start firewalld
- 关闭服务:systemctl stop firewalld
- 重启服务:systemctl restart firewalld、firewall-cmd --reload
- 查看服务状态:systemctl status firewalld、firewall-cmd --state
- 开机自启服务:systemctl enable firewalld
- 开机禁用服务:systemctl disable firewalld
- 查看是否开机自启:systemctl is-enable firewalld
NAS端安装FRPC
- 下载安装docker
- docker注册表,选用frpc 0.26.0版本(可自行选择容易下载的版本,但服务端frps必须对应同版本或者同大版本号的,如:0.34.1的话,可以用0.34.2)
- docker注册表下载后,在映像中可以看到。选择映像中的frpc进行启动编辑,启动编辑省略,可以参考github中的导航说明。
- 配置frpc.ini,本次基于frpc 0.26.0版本
《frpc.ini》文档
[common] server_addr = xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx # 服务器地址 server_port = xxxx # 服务器端口 privilege_token = xxxxxx # token = xxxxxx 有些服务端版本采用这个字节,多数采用“privilege_token”字节,token理解为密码 protocol = tcp [http] type = http # http协议orhttps协议,如果两个都要的话就单独复制一段[https] local_ip = 192.168.x.xx # 群晖的内网IP local_port = xxxxx # 你自己的web服务器端口 custom_domains = xxxxxxx.xxx # 如果你有自己的域名,可以设置你自己的域名,先将自己的顶级域名解析到frp服务器域名(如二级域名的话用CNAME记录,不要用A记录) #subdomain = nas # 全局下唯一的子域名,你的访问地址将会是http://subdomain.xxx.xxx,服务器端必须已绑定顶级域名,否则不要设置; # 此外,顶级域名需要在域名系统上做好CNAME的泛解析,否则不可用。HOST:*.xxx.xxx;Value:xxx.xxx。 [ssh] type = tcp local_ip = 192.168.x.xxx local_port = xxxxxx # 需要转发到的端口,ssh端口默认是22 remote_port = xxxxxx # frp服务端的远程监听端口,即你访问服务端的remote_port就相当于访问客户端的 local_port,如果填0则会随机分配一个端口 #[DSM] # type = tcp # tcp协议 # local_ip = 192.168.x.xxx # 127.0.0.1指穿透本机,也可以填写群晖内网IP. # local_port = xxxxxx # 群晖内网HTTP端口,默认为5000. # remote_port = xxxx # 映射到外网端口,暴露给服务器,这个客户端必须唯一 # subdomain = nas # 全局下唯一的子域名,你的访问地址将会是http://subdomain.xxx.xxx,服务器端必须已绑定顶级域名,否则不要设置; # 此外,顶级域名需要在域名系统上做好CNAME的泛解析,否则不可用。HOST:*.xxx.xxx;Value:xxx.xxx。
搭建手记
大鹿搭建frp反向代理服务的背景:
- 一台私有nas需要安装在农村老家的东方有线光纤宽带下,而经过确认和尝试,获取的DDNS是111.214的,也就是东方有线的私网,无法穿透。
- 和东方有线在自家院子里冒着12月的寒风电话沟通三巡,无法提供公网IP,哪怕是动态的,似乎他们的客服完全不懂,此处万马奔腾……
- 晚上在网上查询了多种方法,其中花生壳的付费和硬件模式(花生棒、花生盒子)想过尝试,但是最终还是不能接受这种太过受制于人的方式。
- 最终发现了frp这个从不知道的事物。初步构想是在晚上躺在农村的床上想到的:企业固定IP + 自建的CentOS,或者上海市区的电信公网IP(市区里装的早,刚发现提供了公网IP,良心!)两套方案,最终决定第一种。
- 周末后周一到公司,利用非工作的午休和晚间时间,启动了安装和搭建调试:
- NAS搭建docker以及docker容器的frpc;
- CentOS本来是当热备机和bbs服务器的,负载几乎是0.x%级别的,所以通过内网ssh搭建了frps;
- CentOS开放firewall;
- AF开放frps端口;
- 当晚宿舍调试握手,成功!
- 第二日,记录了本次搭建和调试的笔记,或许哪一天我的孩子或者朋友需要参考。
2021/12/1后记
- 将自家一台闲置的G41主板GAMEMAX机箱的主机做成了群晖NAS,需要同时请求Centos的FRP代理.
- 产生的问题就是FRPS的http类监听端口只有各一个(http、https),而处于app需求,每台nas都需要占用http两个端口。
- 如何实现两台nas的代理需求困扰了两天,尝试了网上数个谬误的推荐,本人也不清楚博主最后是否运行稳定了多久……
- 谬误1:取消frps端vhost监听,使用frpc的remote_host访问……,其实从原理上就是不可能的;当然,大鹿在当时无计可施情况下也试了几次,失败;
- 谬误2:不使用type=http,改为type=tcp……,协议上来讲tcp和http协议是有区别的,如果偶尔成功了也只能说是基础协议层面的bug类问题,我尝试过,但是最后还是不稳定放弃了。
- 最终使用了如下方案:
- 域名服务启用CNAME泛解析,HOST:*.xxx.xxx;Value:xxx.xxx;
- FRPS启用:subdomain_host;
- FRPC启用:subdomain。
- 目前为止其中一台nas成功启用frp服务,另外一台在本周更新frpc和docker,因为设备在100多公里外:)
2021/12/6多http及ssh服务的问题解决
- 上周将第二台接入后,第一台无法联机,怀疑还是配置问题。回家后还发现NAS的电源出问题了,似乎是损毁了。
- 重新购买电源,更换后还是无法使用subdomain登陆。
- 经过多轮调试和查询FRPS服务说明文档,今天问题发现并解决,属于多台客户端的frpc配置重定义问题:
- 多台frpc中[common]定义不用变化;
- 多台客户机frpc中[http]、[https]、[ssh]等协议代理请求中不能使用重名。比如使用http和ssh的:
- [http-1]、[http-2]、[https-1]、[https-2];
- [ssh-1]、[ssh-2]。
- 以上修正后,所有访问正常,其他协议类定义可以推断同样依次类推。
- 注意:务必要在FRPS和FRP中定义:<subdomain>。
- 其实从理论上也可以理解,如果协议的代理请求是同样[ID],FRPS服务器确实如何去识别这是谁的要求呢?
- 自此,多台frpc的代理服务配置完成,结案。
- 总结:所有的开发源代码的应用,多参照说明文档,少看网络上那些假大神的瞎捣鼓,看还是要看看,走走弯路也可以学到知识。